Table of Contents
Clone
Creates a copy of the spectrum. The input G1 = G2 creates two pointers to the same object. Changing G1 will change G2. G1=Spectra.Clone(G2) will create two different objects.
Example
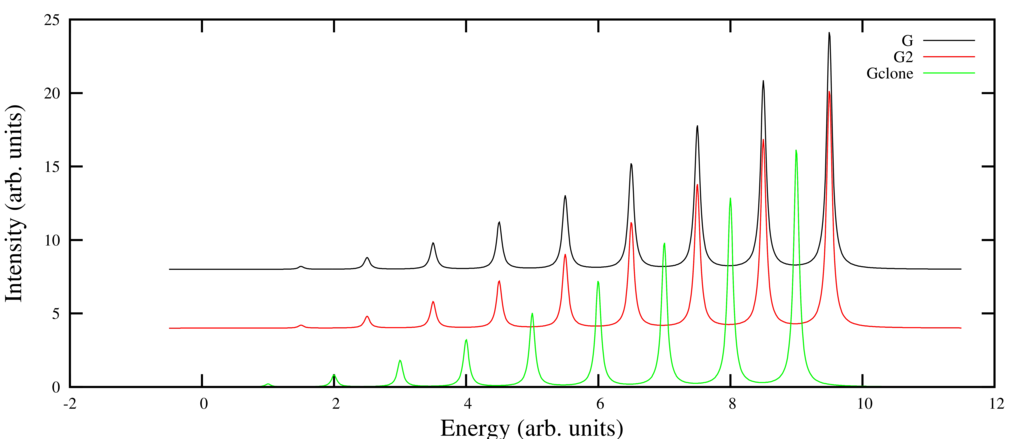
The following example creates a clone of G and stores this in the variable GClone. Next it sets G2 equal to G. Shifting G2 will also lead to a shift in G. GClone is independent of G.
Input
- Example.Quanty
dofile("definitions.Quanty") GClone = Spectra.Clone(G) G2 = G G2.Shift(0.5) G.Print({{"file","Spectra.dat"}}) G2.Print({{"file","Spectra2.dat"}}) GClone.Print({{"file","Spectra.Clone.dat"}}) gnuplotScript = gnuplotHead .. [[ set output "Spectra.Clone.ps" plot "Spectra.dat" using 1:(-$3+8) title 'G' with lines ls 1,\ "Spectra2.dat" using 1:(-$3+4) title 'G2' with lines ls 2,\ "Spectra.Clone.dat" using 1:(-$3) title 'Gclone' with lines ls 3 ]] file = io.open("Spectra.Clone.gnuplot", "w") file:write(gnuplotScript) file:close() os.execute("gnuplot Spectra.Clone.gnuplot") os.execute("convert -density 1024 Spectra.Clone.ps -resize 1024 Spectra.Clone.png")
Result
The resulting picture is: